Profit forecast – how to determine your company’s chances of success
Does your investment pay off in terms of results? A profit forecast (also known as a profit report) will answer this question. To do this, you need to compare the forecasted turnover with all expected costs and calculate the medium-term success of your company. The profit report is part of the financial plan and is included in the business plan.
Purpose of the profit forecast
The profit forecast in the context of business start-ups is of particular importance. With the list, founders demonstrate the viability of their business idea to third parties. Banks in particular require a corresponding calculation which shows that the expected profit both covers the living costs of the founder and is sufficient to pay interest and repayment instalments.
A detailed profit forecast therefore helps you:
- Estimate the success of your investment
- Convince investors of your company’s economic viability
- Demonstrate the viability of your business
You can also use costing to identify goals and set milestones. Keep an eye on these in order to be able to take timely countermeasures in the event of deviations from the calculated target figures.
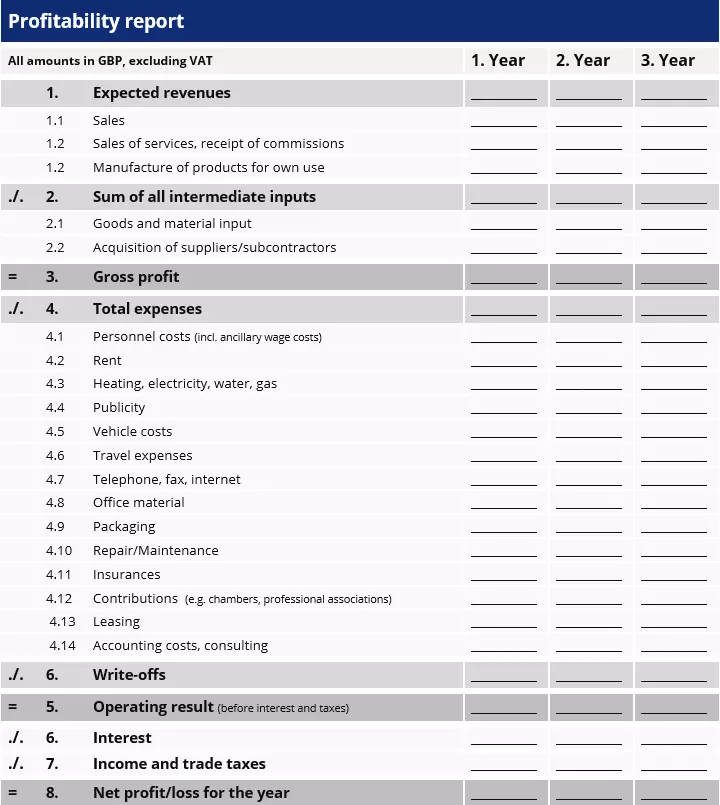
The profit forecast is a set of figures included in a business plan. It is part of the financial plan and compares the net turnover of a company with all expenses for goods and equipment. The result of the profit forecast is the operating income before taxes, depreciation, and interest.
Profit planning
Proceed with profit planning in two steps:
- Prepare a profit report: Determine the expected operating profit on the basis of sales planning and a cost forecast for the next three fiscal years.
- Evaluate profit report: Check whether the calculated operating profit covers interest and taxes.
To create a profit forecast and evaluate it objectively, you need the following statements:
- Sales and cost plan
- Resource plan
Creating a profit report
The core of profit planning is the earnings forecast: the comparison of expected sales and costs. The calculation is based on previously created sales and cost plans.
A sales plan is a precise forecast of the expected sales of your company. The plan should cover a period of three years and should be based on official industry figures, especially for start-ups. If you subtract the expected costs for the use of goods and materials from the sales forecast, you get the expected gross profit for the respective planning period. While established enterprises can use the turnover and cost planning from the profit and loss accounts of previous years, new founders must provide the forecast on the basis of estimated projections.
First indications for the turnover forecast are provided by inter-company comparisons. The average turnover for a respective sector should then be adjusted to the individual circumstances with the aid of market and competition analyses. Relevant factors include the location, the competitive situation, necessary advertising efforts, and price expectations of customers and competitors. As a rule, founders resort to professional help when forecasting sales.
A financial plan is a statement of all current costs for a company – for example, expenses for personnel expenses, rent, advertising, or travel expenses. The difference between gross profit and operating costs is the operating income before taxes and interest. If these expenses are subtracted, the net income for the year is obtained. A negative result is called a net loss for the year.
Once you have the required plans and statements, compile the figures according to the below profit report template.
Basic outline of the profit report
The following must be done when drawing up the profit forecast:
- List net sales, revenues and expenses, excluding VAT
- Display the sales of different lines of business separately
- Specify personnel costs, including all non-wage labour costs.
While interest is to be shown as a cost in the profit forecast, redemption installments are not taken into account. The latter are to be paid from the net income for the year.
The profit forecast refers exclusively to the business enterprise; private payments and receipts are not included in the list.
Evaluate the profit forecast
In order to objectively estimate a company’s annual surplus, you should determine how much profit you need to make to cover your own living expenses. To do this, create a separate capital requirement plan for private expenses.
The calculated net income for the year should cover you, and, if applicable, your family’s living expenses and should also be sufficient to pay the payment instalments of any loans or lines of credit.
Tips for a successful start-up
Business start-ups are generally dependent on borrowed capital. The figures in the business plan therefore play a central role. When it comes to convincing investors of the planned business’s profit, you must not make any mistakes in the profit calculation. We advise you to:
- Create a profit forecast based on a sound sales and cost plan
- Use the principle of prudence as a basis for your costing: If you have room for manoeuvre in your assessment, you should tend to set costs higher and sales lower
Please note the legal disclaimer relating to this article.