What is the deep web?
Not all content on websites or online stores is freely available to users and search engines. Such restricted-access content falls under the banner of the ‘deep web’. The reasons for access restrictions can be manifold.
- Free website builder with .co.uk
- Free website protection with one Wildcard SSL
- Free 2 GB email account
Deep web: definition
Most people are probably not familiar with the ‘deep web’, but it is the generic term for the type of data you cannot access via a search engine or by typing in the URL. This includes information such as company databases, and universities and museums that can only be visited via a login. Bank accounts, shopping baskets, user accounts of online shops and many more fall under this banner. Strictly speaking, the deep web includes the dark web, but the content differs significantly.
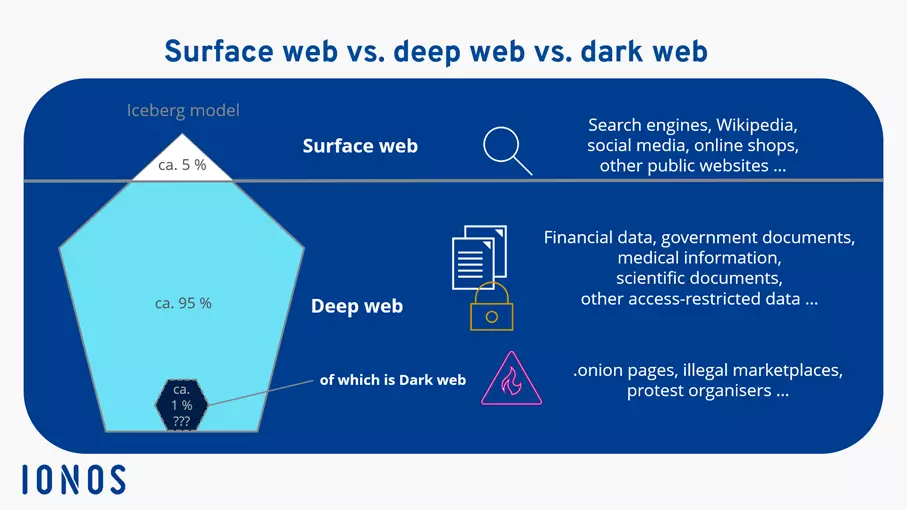
Differences between the deep web, dark web, and the Internet
Let's begin with a clear definition of the Internet as we know it. All search engines, news sites, online stores, and websites that we access through a browser such as Chrome or Firefox and that do not require logins to be viewed are part of the surface or visible web. The transition from deep to visible web is fairly fluid with some content of the surface web also belonging to the deep web.
The deep web accounts for a significantly larger share of the Internet and includes all restricted content. Google and other search engines cannot index this data.
The dark web is nestled within the deep web. Access is more heavily regulated and only possible using specialist technologies. Due to restrictions and anonymity of the dark web, it is unfortunately a magnet for criminal activities. In the following paragraphs, deep web refers only to the content described in the previous paragraph, not that of the dark web.
Why content is hard to find on the deep web
One reason why deep web content is rarely found or indexed by search engine crawlers is due to its access restrictions. Terms of use agreements or payment barriers are additional obstacles. In these cases, the user can only reach the respective URL if they previously entered a password or paid to access a page.
There’s another reason why content on the deep web is difficult to find. Even if you know the URL of the page you want to access, sometimes search engine crawlers may not be able find or index the site in question. The reasons for this are manifold.
For one, webmasters can exclude content from being indexed by using the Nofollow command. Secondly, a page could be hidden in such a way that the crawler cannot find it. For each website, the crawler has a dedicated ‘page budget’. Once that is exhausted, sites on a lower level are not taken into account. A third possibility is a lack of technical requirements for indexing, for example, if Flash is used.
What deep web content means for your website
In principle, deep web content does not pose a problem for you or your website visitors. On the contrary, these pages tend to be found on almost every major website and users simply use their login to access them.
However, lack of Google indexing can affect a website when it comes to search engine optimisation. Plenty of scientific or medical content, for example, tends to be access restricted. It is a well-known problem in the scientific communities because the goal of science and information should be to make content freely accessible and indexable (as long as laws and company policies allow for it). At the very least, landing pages should be designed in a way that search engines get an idea of the content on a website.