How to boot your Mac in safe mode
If your Mac no longer works properly or has problems booting, it’s often quite difficult to determine what the cause is. Mac safe mode is intended as a useful tool for diagnostics and first repairs, allowing you to change faulty settings and – if necessary – remove programs that cause problems if the standard system boot fails. How does this feature work and how can you start your Mac in safe mode?
What is safe mode on a Mac?
The safe mode in operating systems like macOS helps to analyse problems and errors that disrupt or prevent normal system processes. Here, the auto-start programs are not run and a number of additionally installed programs and system fonts are temporarily deactivated. Since most applications and processes don’t automatically start in safe mode like they do in standard mode, users can successively test which software, settings, and drivers may be causing the problems or errors.
Before starting your Mac device in safe mode, it’s worth taking a look at the Mac task manager. This tool provides a detailed look at active processes and the effect on your Mac’s performance, enabling you to find the cause of existing problems in some cases.
When you boot your Mac in safe mode, many useful background tools will also be run that automatically diagnose problems and attempt to carry out repairs. What’s more, the system cache is cleared so that the Mac can reassign it when it’s restarted in normal mode. No longer required cache files of application programs are also deleted to optimise the storage space on the data media used.
How to boot a Mac in safe mode
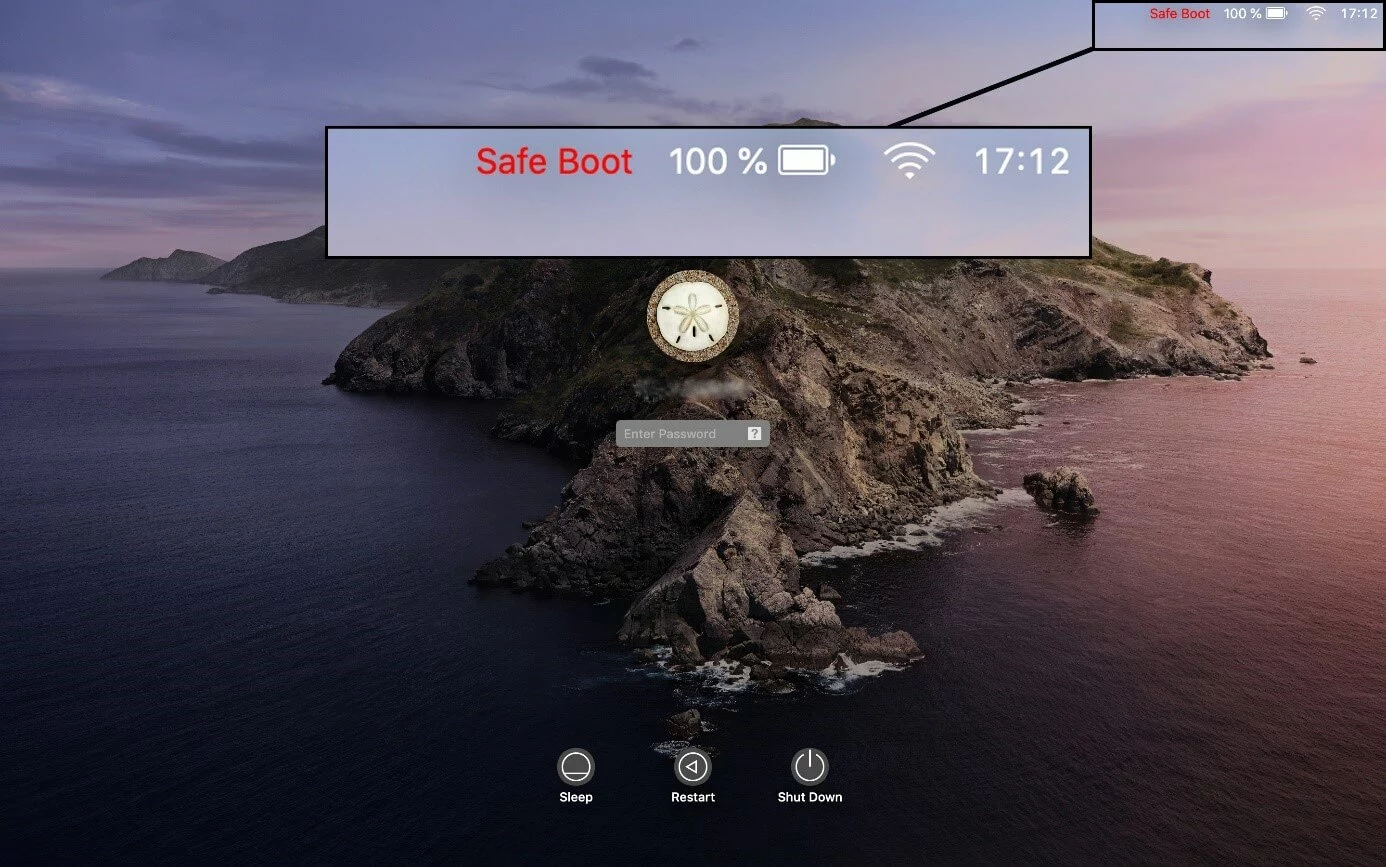
To start your Mac in safe mode, hold down the shift key while booting the device until the Apple logo appears.
On the login screen, you’ll then see that your Mac is in safe mode. In the top-right corner, ‘Safe Boot’ will be shown in red font next to the keyboard layout and power display (only for MacBooks, MacBook Pros, and MacBook Airs).
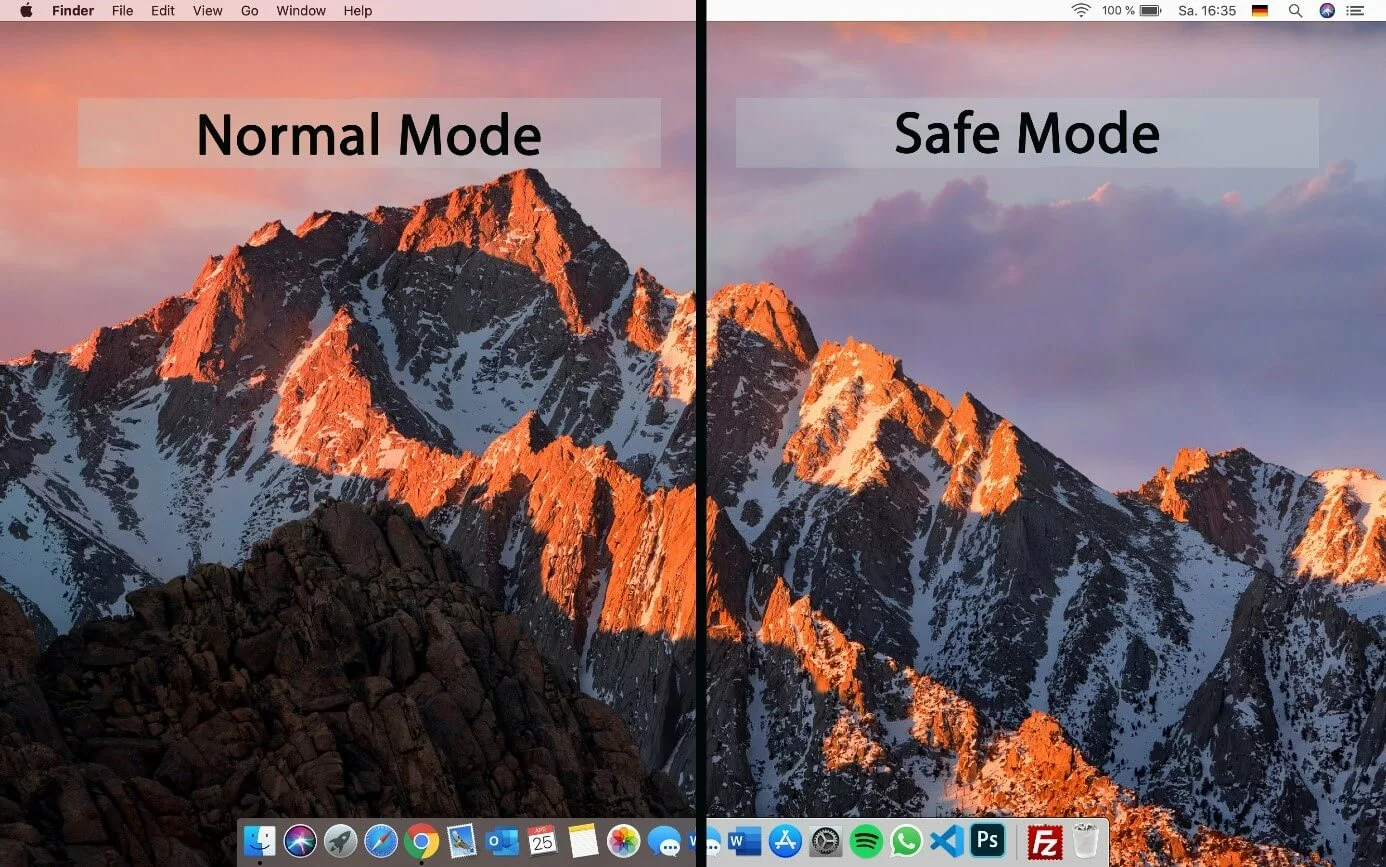
While the task bar and dock appear transparent in normal mode, this is not the case in safe mode.
The login process can take longer in safe mode, since the system automatically searches for errors.
If you can no longer start your Mac normally, you can also activate safe mode via the Terminal. Simply open the command line tool (Terminal) and enter the following command:
sudo nvram boot-args="-x"After the errors have been successfully resolved, safe mode can then be closed with the command below:
sudo nvram boot-args="-x -v"If you have activated or use the encryption feature FileVault, you will not be able to access safe mode via Terminal.