Accessing the BIOS: How does it work?
The Basic Input/Output System (or BIOS) is the backbone of your computer system. Nothing works without it. BIOS ensures the smooth running of the most fundamental functions of your PC or laptop. Without it, even the operating system won’t load. Most people only come in contact with the BIOS when something stops working. It’s not until Windows no longer launches when many users begin to ask: How do I access the BIOS?
When using the BIOS, remember that any changes you make could have fatal consequences for your system and, in extreme cases, even stop your computer from working. The BIOS is also not particularly user-friendly. It’s therefore essential to exercise caution whenever making changes to it.
Accessing the BIOS is not only helpful when your computer breaks down. The system gives you options that you can’t find in the Windows user interface. Many adjustments to the hardware are usually done from the BIOS. Users can configure computer components to speed up the performance of their computer. For example, the BIOS can be used to overclock the CPU. You can also enter the BIOS to make system launches faster.
Entering the BIOS: the individual steps
The BIOS essentially starts running as soon as you boot a computer. In fact, the device wouldn’t work without it. This important system ensures that other software on a computer can be loaded. It solves an interesting problem: for the computer to start a software programme, another software programme has to tell it to launch the software. The BIOS is located on a storage module independent from the power supply and therefore runs immediately after switching the computer on. It provides instructions to launch the entire system.
Ideally, you should never have to access the BIOS. That’s why entering the programme is not very intuitive. BIOS is only intended to start the actual operating system and all the necessary components. Computer manufacturers therefore only allow the BIOS to be launched for a few seconds when booting the system. When the computer boots, a screen message will indicate a certain key that has to be pressed to open BIOS. You will usually have just enough time to do so before the start screen of the operating system appears.
Many systems no longer use the BIOS in the strictest sense. However, its successor – called the Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) – offers many of the same functions and is therefore often referred to as a BIOS.
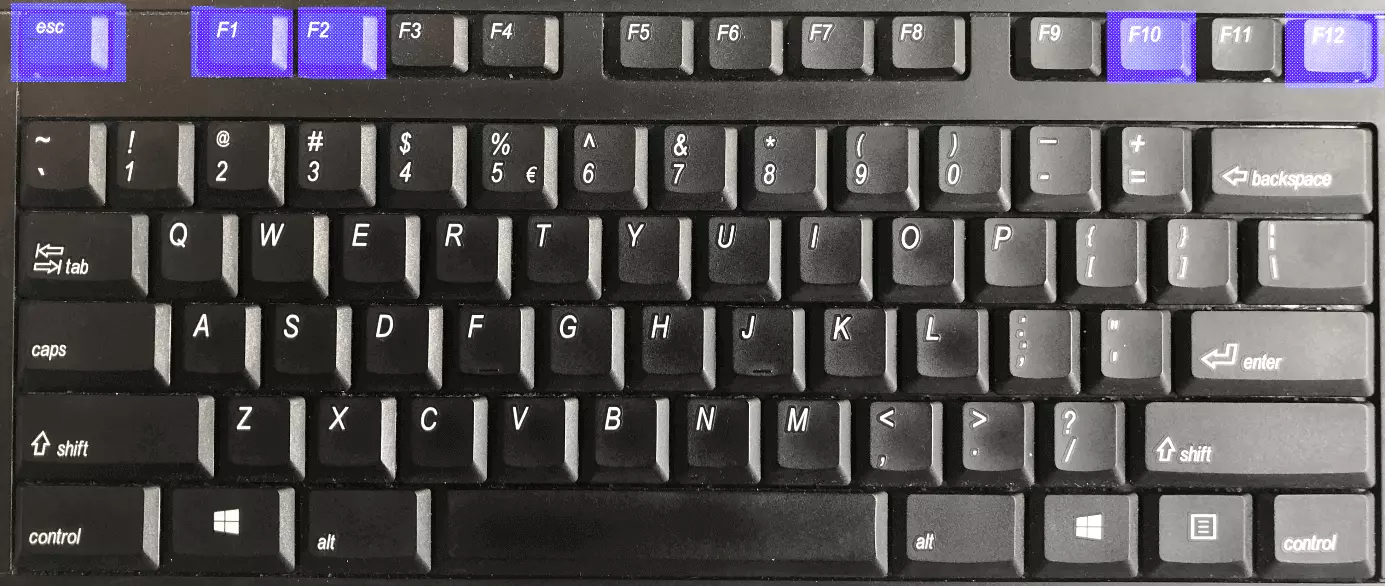
Which key you need to press in order to access the BIOS is determined by the device manufacturer. But certain keys are more frequently used for this purpose than others. They include: [Del], [Esc], [F1], [F2], [F10] or [F12], among others. Sometimes, particularly with older systems, the key combination [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Esc] is used. The table below includes a list of typical BIOS keys according to different manufacturers.
| Acer | [F2] / [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Esc] |
|---|---|
| AMIBIOS/American Megatrends | [Del] / [F1] |
| Asus | [F2] |
| Award-BIOS | [Del] / [F2] / [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Esc] |
| Compaq | [F10] |
| Dell | [F2] |
| HP | [F10] |
| Packard Bell | [F2] |
| Phoenix-BIOS | [Del] / [F2] / [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Esc] |
| Sony | [F2] |
| Toshiba | [Esc] / [F1] |
In certain circumstances, the key required to open BIOS can vary for an individual manufacturer depending on the respective product line.
Windows: accessing the BIOS
The newer operating systems Windows 8 and 10 now offer an option to access the BIOS without having to act during boot-up of the system. The Boot Options menu now allows you to enter the BIOS from within the operating system. However, the computer needs to be restarted from Windows to do this. Before hitting the restart button, hold down the [Shift] key. While the system reboots, the normal Windows start screen will not appear, instead the Boot Options menu that provides access to the BIOS will open up.
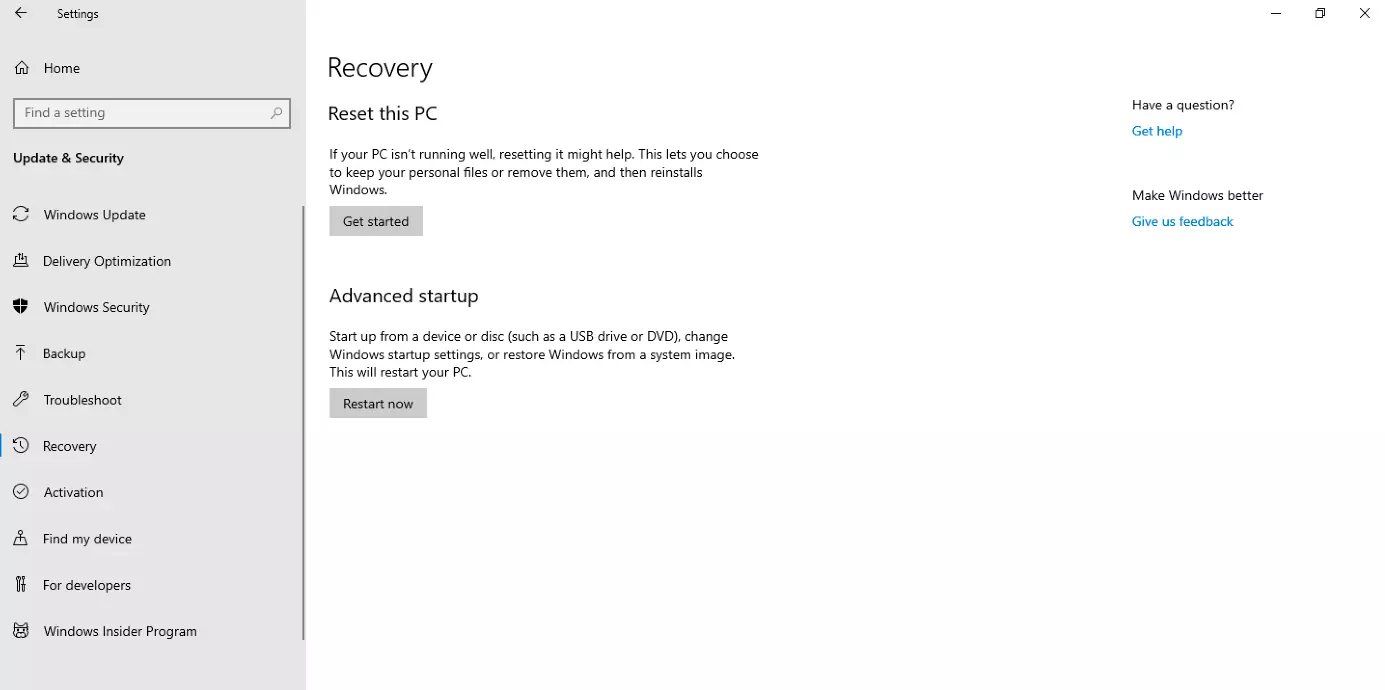
An alternative way to open the boot menu is via the system settings. After selecting the category “Update & Security” and pressing the “Recovery” tab, you can click on “Advanced Startup”. The system will then restart and you will be shown the Boot Options menu.
Is your system already getting on a bit? Maybe it’s time to run a BIOS update.