What is a Hostname?
The hostname is what a device is called on a network. Alternative terms for this are computer name and site name. The hostname is used to distinguish devices within a local network. In addition, computers can be found by others through the hostname, which enables data exchange within a network, for example. Hostnames are used on the internet as part of the fully qualified domain name.
- Free website protection with SSL Wildcard included
- Free private registration for greater privacy
- Free 2 GB email account
Differentiation between hostname, domain and fully qualified domain name
The hostname is a freely selectable name for a host. For example, you could call a server in a company network responsible for the central administration of emails “mail” or “mail123”.
However, if a computer needs to be available over the internet as well as locally, the hostname needs to be supplemented by information that indicates what part of the internet the computer is located in. In the internet, computers can be uniquely assigned using a combination of hostname and domain. These uniquely identifiable name chains are known as a “Fully Qualified Domain Name“ (FQDN). An example of an FQDN would be:
mail123.example.com.
If you read the terms of the hierarchy from right to left, you can recognise the components of the FQDN in the following order: root label (empty), top level domain (.com), second level domain (example) and hostname (mail123).
An FQDN is a human-readable form of addressing. Unlike humans, computers work with numerical IP addresses to uniquely identify computers on the internet. Within the framework of a website visit, an intermediate step is necessary so that the alphanumeric domain can be translated into a numeric IP address.
The domain name system (DNS) is responsible for this name resolution. The entered domain is assigned to the corresponding IP address and then the searched-for page is called up. The purpose of this system is so that humans do not have to enter the IP address every time they visit a website, but can use a name that will be easier to remember instead.
Explaining a hostname with some examples
In the following example, both the individual hostname and the complete fully qualified domain name are given.
In the URL www.ionos.com, the hostname is www. This is the conventional, albeit not-mandatory name for web server.
Servers that are specifically designed to access web pages on mobile devices usually the hostname m, like m.example.com.
Mail servers are often named after their function or the protocol used and receive a corresponding hostname like mail, pop3 or imap.
In other cases, the hostname refers to a specific country. In online shops, for example, it is not necessary to use a new top-level domain every time you want to refer to a specific country. This is also possible through the hostname. An example of this is in regards to Germany is the de in de.onlineshop.net.
Looking for an alternative to the traditional .co.uk extension, or want to grow your online presence? Give .uk a try today.
£1 for 1 year!
Do not confuse the hostname with a subdomain. This is also located to the left of the top-level domain, but does not designate a computer or server, just the domain area. The hostname is still far on the left. Example: In the FQDN www.example.ionos.com, “IONOS” denotes a domain name, “example” denotes a subdomain and www is the hostname.
Find out your hostname in Windows
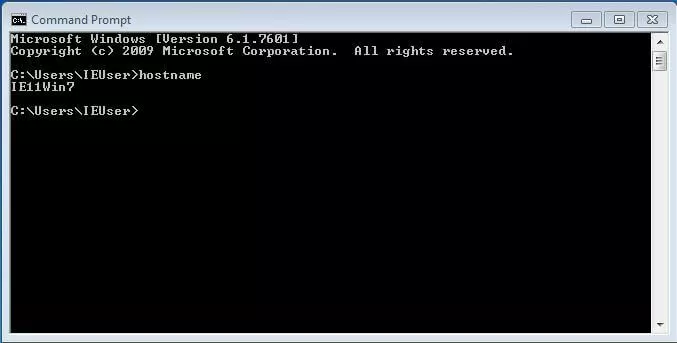
The easiest way to display the hostname of a Windows computer is to open the command prompt, enter the following code and press “Enter”.
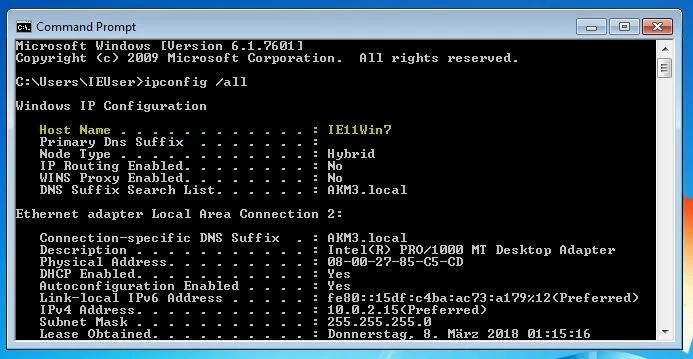
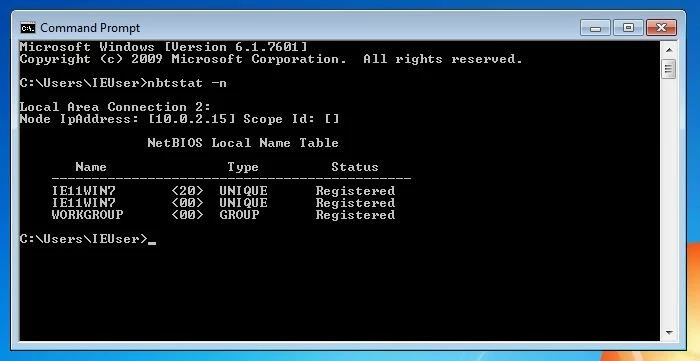
hostnameipconfig /allEntering the following command also results in the output of your own hostname. Then include the line “UNIQUE”.
nbtstat –nChanging the hostname in Windows
To change the name of your computer, you need to leave the command line again. With Windows 10, press Windows + X and select “system”. Now click on “change settings” at the bottom right and then on “change” in the opened window. Enter the desired name in the “computer name” field and press “OK”. The change takes effect when you restart your computer.
Alternatively, you can also select “all settings” in the notification area and click on “system” there. Under “info” you will find the field “rename PC”. A click on it takes you to a window where you can change the name of the PC.
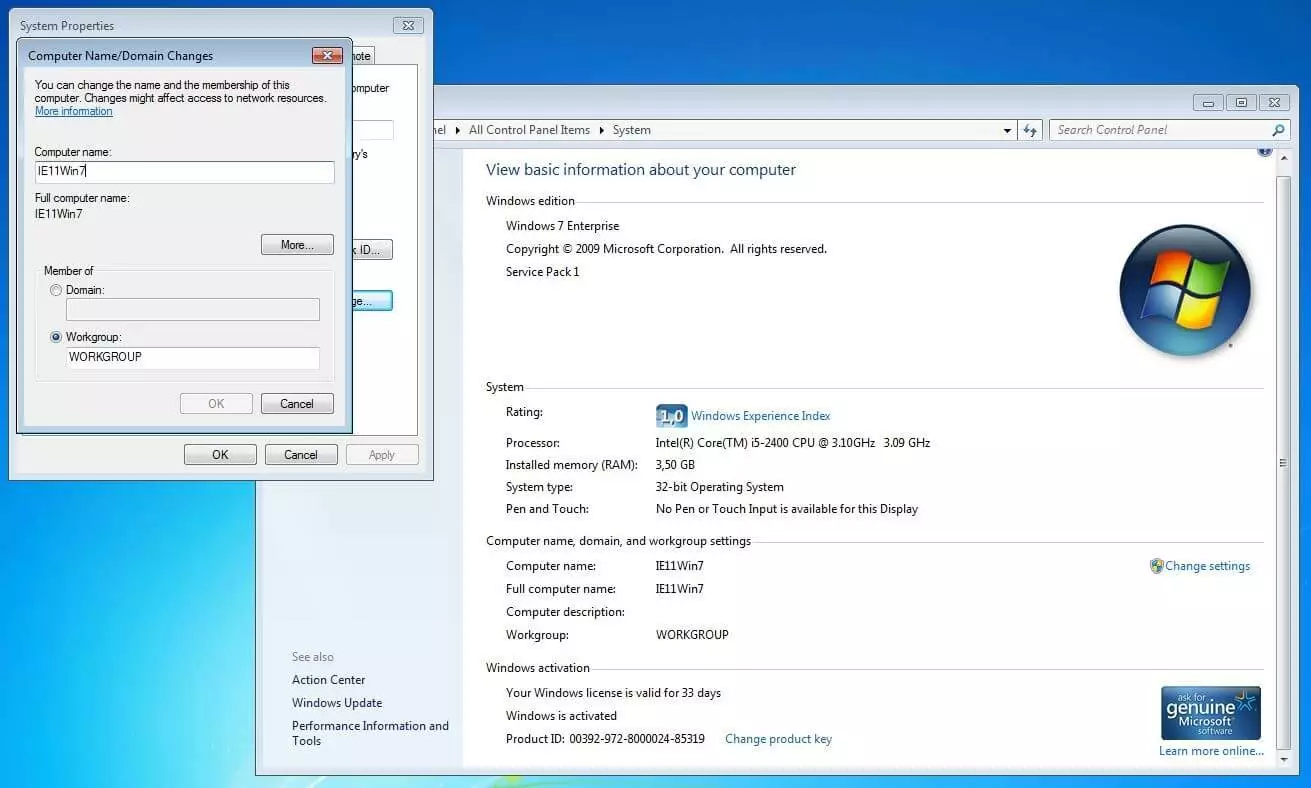
In Windows 7, go to the “start menu” to change the name and right click on “computer” and select the category “properties”. The penultimate section shows the computer name that can be edited by clicking on “change”. In Windows XP, the computer name is also changed under “properties”. To do this, right-click on “my computer” in the start menu and select “properties”.
Find out and change the hostname in OSX
To display the hostname in OSX, select “system settings” in Apple. Then click on “share”. You will now see the hostname in the “computer name” field. It can also be processed there. To make the change visible in the terminal and in the network, restart the computer after saving the new name.
Find out and edit the hostname in Linux
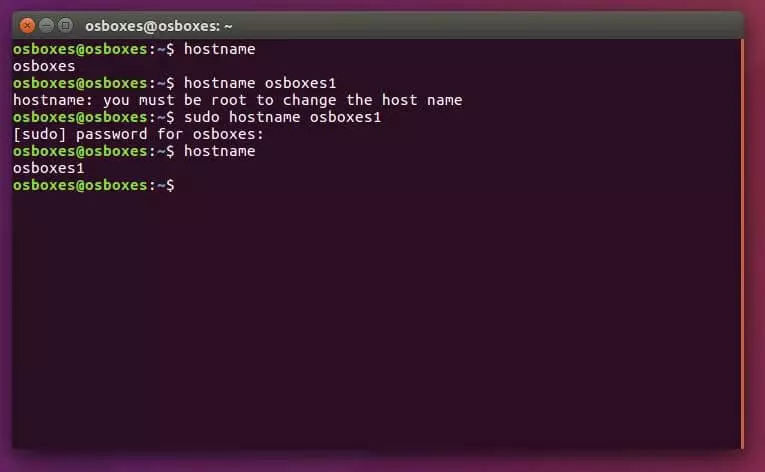
To find out the hostname in Linux, enter the following in the terminal, just like with Windows:
hostnameChanging the name until the computer’s next reboot is also dine with a simple input:
sudo hostname new_NameChange the hostname permanently with Linux
/etc/hostnameThis can be edited in the editor. If you execute the following script, you can apply the change directly:
/etc/init.d/hostname.shIn RedHat-based systems, the hostname can be found in the following file, among others:
vi /etc/sysconfig/networkThere you can change the hostname in the following line:
HOSTNAME=new_NameEnter your chosen new hostname instead of new_name. When the script is executed,
/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinitThe change takes effect immediately.
Determining the hostname from the IP address
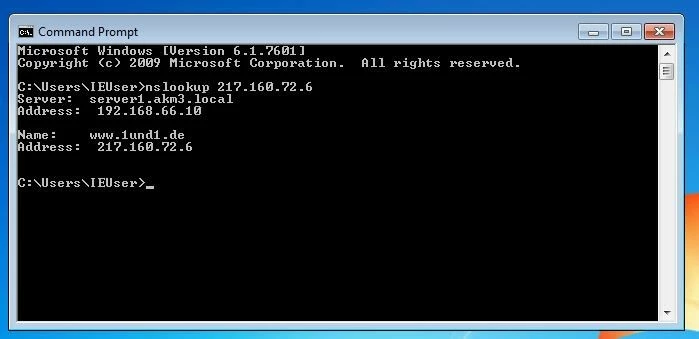
Sometimes, the only IP address is only available if the computer is in a network, so a hostname would help identify a computer faster. To find out the name of a computer by its IP address, you can use the command “nslookup”.
To do this, type the following into the command line:
nslookup %ipaddress%