“ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED”: how to fix this DNS error in the Google Chrome browser
The internet gives you access to a seemingly unlimited number of websites of all kinds. All you need in order to access a particular web project is an internet browser and the project’s domain name. You type the domain name into your browser’s address bar to represent the page’s numerical IP address. DNS servers (Domain Name System) handle this automatic translation which is referred to as domain name resolution. If the domain name cannot be resolved, you will inevitably encounter errors, which prevent you from accessing the website. When this happens, the Google Chrome browser will display the error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED”.
In the following sections, you will learn more about what might cause DNS domain name resolution errors. We will also provide you with the best troubleshooting solutions for fixing the Chrome browser error “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED”.
- Free website protection with SSL Wildcard included
- Free private registration for greater privacy
- Free 2 GB email account
What does the error message “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” mean?
When you receive the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error message, Chrome is saying that it could not find the IP address which matches the website domain name you entered. If this has happened, you will not be able to access the page since the IP address is required to establish a connection with the web server. You can encounter this error regardless of whether you are using Chrome on a desktop PC (Windows, macOS or Linux) or on a mobile device (Android or iOS). This error is not exclusive to the Chrome browser; you can also encounter this error on other browsers, such as Firefox or Safari. However, they will display a different error message than Google Chrome if the DNS fails to resolve the domain name when trying to access a website.
Possible causes for the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error
There are a number of reasons why a DNS domain name resolution might fail. One of the more common reasons is that the DNS server is (temporarily) unavailable. In this situation, if there are no entries for the website you are trying to access in your browser cache or in your operating system’s DNS cache, the DNS will not able to resolve the domain name. The previously mentioned address entries can also be a possible cause themselves for the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error in Chrome. For example, this error can occur if the browser tries to answer a DNS query using a cached address when the IP address has since been changed.
Other possible causes of this error include router problems, incorrectly configured internet settings, Chrome’s prediction function for faster page loading, malware and faulty security software.
How to fix the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error in Chrome
Since there are many different reasons for why you may have encountered a DNS problem, there is no universal solution. However, if you still want to try to tackle the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error message on your own, we will cover the solutions that have the highest chances of working in the following sections.
Solution 1: restart the router
Before you start fiddling with the settings for Chrome or your operating system, you should first check the router connecting your device to the internet. Even if it looks like the internet connection is fine, there is still a chance that this might not be the case. Therefore, you should restart the network device for a possible quick and easy solution to the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error. To restart the device, disconnect the power supply for at least 30 seconds by unplugging the power cable. Then, reconnect the router to the power supply.
If you have temporarily disconnected the router from the power supply, it will take a while for it to fully resume operation after you reconnect it. Wait for the internet/DSL light to turn green before testing whether the DNS problem has been fixed by restarting the router.
Solution 2: delete your browsing data
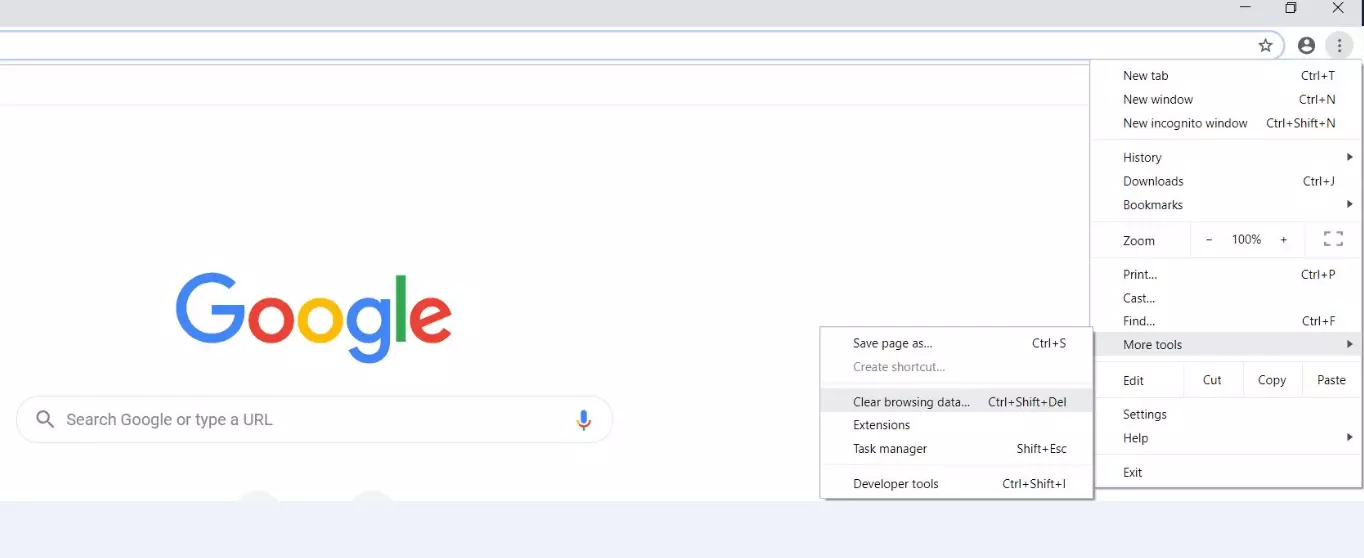
Chrome saves data on all the websites you have visited in the past by default. This cached data helps pages load faster when reloading them and auto-completes addresses as you type. As useful as this function is, it can quickly become a problem and result in the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error when using Android, Windows, and so on. A possible solution is thus to delete all your browser data. To do this, open the Chrome menu using the three-dot icon and select “More tools”. Then click “Clear browsing data”.
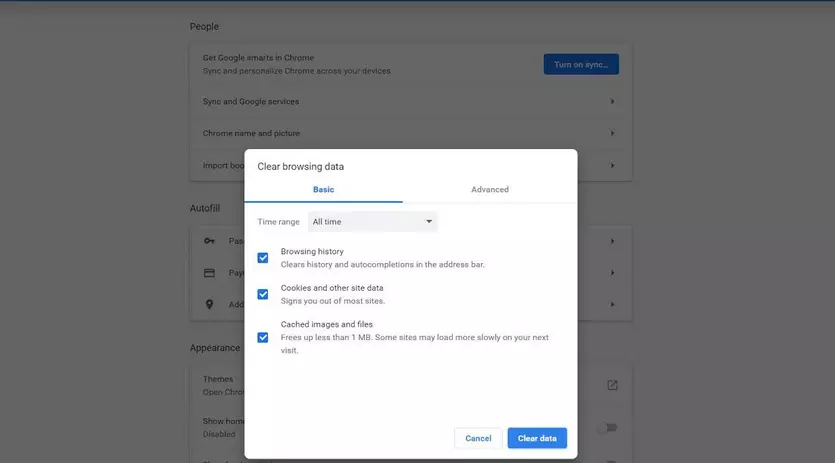
Now, select the types of browser data Chrome should delete from the cache, with “Browser history” and “Cookies and other site data” being a must. You should also make sure that you have selected the “All time” option under “Time range”, otherwise it will only delete your most recent browser history. Once you have made your selection, click “Clear data”.
Solution 3: clear your operating system’s DNS cache
People often only associate cached web addresses with the browser being the user interface for accessing the internet. However, standard operating systems such as Windows, macOS and Linux also have web address books, which automatically cache DNS entries for websites you have accessed in the past. Just like a browser’s cache, the DNS cache can also lead to some errors like the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error in Chrome when the stored entry for an address is incorrect or out of date. In this situation, the solution is also to clear the cache, which is sometimes referred to as a DNS flush.
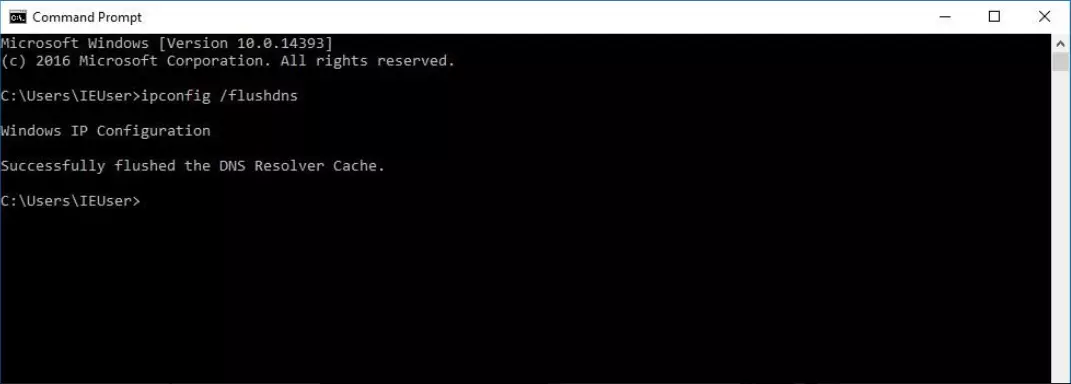
On Windows 10, you can perform a DNS flush by typing a single command into the command prompt window. To do this, first open the Start menu. Then, click the “Command Prompt” option. Alternatively, you can also use the search function to find it. Once you have opened the command prompt window, enter the following command to clear the DNS cache:
ipconfig /flushdnsYou can find more detailed information about the DNS cache and further instructions on how to clear the DNS memory cache on other operating systems in our article on how to flush your computer’s DNS.
Solution 4: reset the Winsock catalogue
If neither the browser cache nor the DNS cache was behind the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” problem, Windows users should take a look at the interface and system application Winsock (also known as Windows Sockets). Winsock helps programs communicate using TCP/IP, and to do so, it creates entries for every connection established. Since this data can also prevent a website from being accessed, resetting the Winsock catalogue is a possible solution to connection problems in the Chrome browser. Just like the DNS flush, you can perform this reset from the command prompt window. However, this situation requires you to run the command as an administrator as described below:
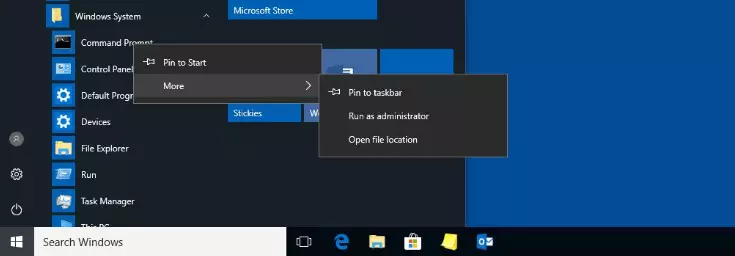
- Open the Start menu by clicking the Windows icon.
- Look for the “Command Prompt” icon located under “Accessories” or “Windows System”, depending on your operating system version.
- Right-click “Command Prompt” and select “Run as Administrator”.
Once you have opened the Windows command prompt window, enter the following command to reset the Winsock catalogue:
netsh winsock resetPress the Enter key to run the command. Then, restart the system to finish resetting it.
Solution 5: change the DNS server
If the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error message is displayed in Chrome because the responsible DNS server is not working, there is not much you can do to fix this. However, it is possible to switch to a different DNS server by configuring your DNS address settings to use the IPv4 or IPv6 protocol. For example, Cloudflare’s public DNS servers are a good choice. These are available at the IPv4 addresses 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1 as well as the IPv6 addresses 2606:4700:4700::1111 and 2606:4700:4700::1001.
On Windows, you can enter these DNS servers, which are designed to be fast and secure, as the default option by following the steps below:
- Open the Control Panel through the Start menu.
- Click “Network and Sharing Center” (in the icon view).
- Then click “Change Adapter Settings”.
- Right-click on the network adapter, which connects you to the internet and select “Properties”.
- Double-click on “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” or “Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)”.
- Enter the above-mentioned addresses under “Use the following DNS server addresses” for the preferred and the alternate server.
- Confirm the changes by clicking “OK”.
The Digital Guide also explains how to change the DNS server on macOS, iOS and Android as well as on older versions of Windows.
Solution 6: disable Chrome predictions
Google Chrome implemented the prediction function to provide faster loading times over the long term. To accomplish this, the function automatically collects information related to any links on the currently open website in order to speed up the load times for those linked pages if you happen to click on one of them. However, this prediction service is known to lead to errors such as the ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED error, so disabling this function in Chrome may solve your DNS problem.
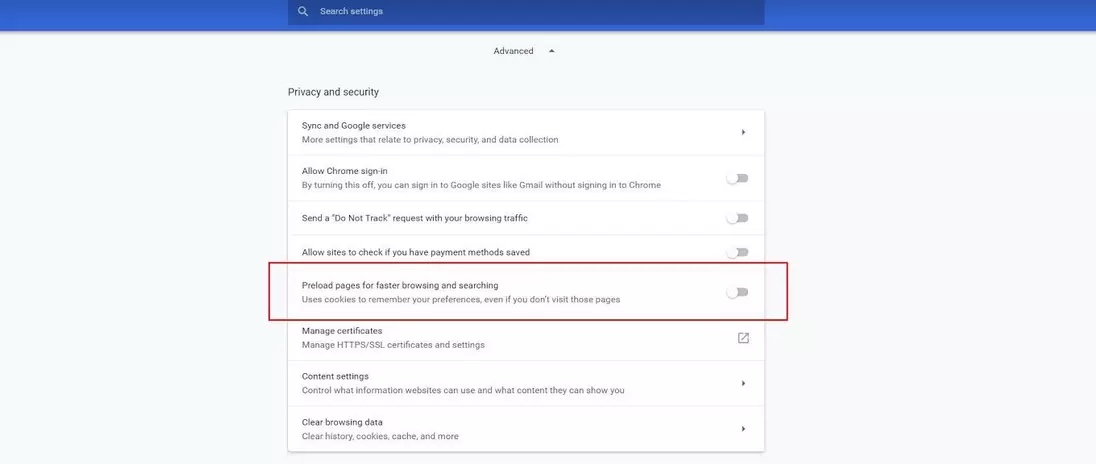
To turn off the prediction function, first open the Chrome menu by clicking the three-dot icon. Then select “Settings”. On the following menu, scroll all the way down the page and click “Show advanced settings”. Under “Privacy and security”, move the slider to the left for the option “Preload pages for faster browsing and searching”.
Solution 7: temporarily disable security software
Any security software you may have installed can also cause the Chrome “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error on Android, Windows and so on. For example, antivirus software or a firewall can prevent access to certain websites, which would result in the browser responding with the error message. You can easily check whether the applications you are using are causing problems like this by temporarily disabling them. If the domain name can then be resolved, you will know that that was the source of the error. If this is the case, you can either contact the faulty software’s publisher or replace it with a suitable alternative.
Solution 8: check for malware
As is the case with many computer issues, malicious software on your system may be the cause of the “ERR_NAME_NOT_RESOLVED” error. For example, malware can change your DNS server configurations, alter your browser history or prevent the domain name from being resolved in some other way. It is therefore important to check your system for a possible malware infection if the solutions described above do not work. Use either your security software or Microsoft’s Malicious Software Removal Tool (MSRT) to perform a scan. It should be noted that the MSRT is only available for Windows users and can only be used with administrator rights.