How to add Google Analytics to WordPress
Google Analytics collects all kinds of data that can tell you about the visitors that come to your website. For example, it groups data on who visits your site and how long they stay, what the demographics of your visitors are and what devices they use.
The information collected can be useful for many different purposes. Content Marketing Strategies can be set up or adjusted based on the most popular posts, pages, products or other content, and it allows for better inbound marketing with a clearer idea of the target audience in order to optimise user experiences and increase your conversion rate. Google Analytics is the best standard tool to consistently optimise the performance of your WordPress site.
Google Analytics & WordPress: three different techniques
Before adding Google Analytics to WordPress, you first have to go to Google marketing platform and click on “Start for free” to set up a new Google Analytics account. Once you do this, Google will give you a tracking code for your website under Admin Tracking information. You can add this code to WordPress later.
In this section, we’ll show you how you can use the tracking code to add Google Analytics to your WordPress website and what you need to pay attention to in terms of data protection.
Google Analytics plug-in for WordPress
The easiest way to add Google Analytics to your website is by using a plug-in. If you do this, you don’t need to change the code of your site. You can choose from several WordPress plug-ins to add Google Analytics to WordPress. We recommend the free GA Google Analytics plug-in from Jeff Starr, which has over 400,000 active installations and an overall 5-star rating.
IONOS WordPress hosting simplifies things – with a range of perfectly matched extensions to make your work easier, you can start putting content on your new WordPress site straight away.
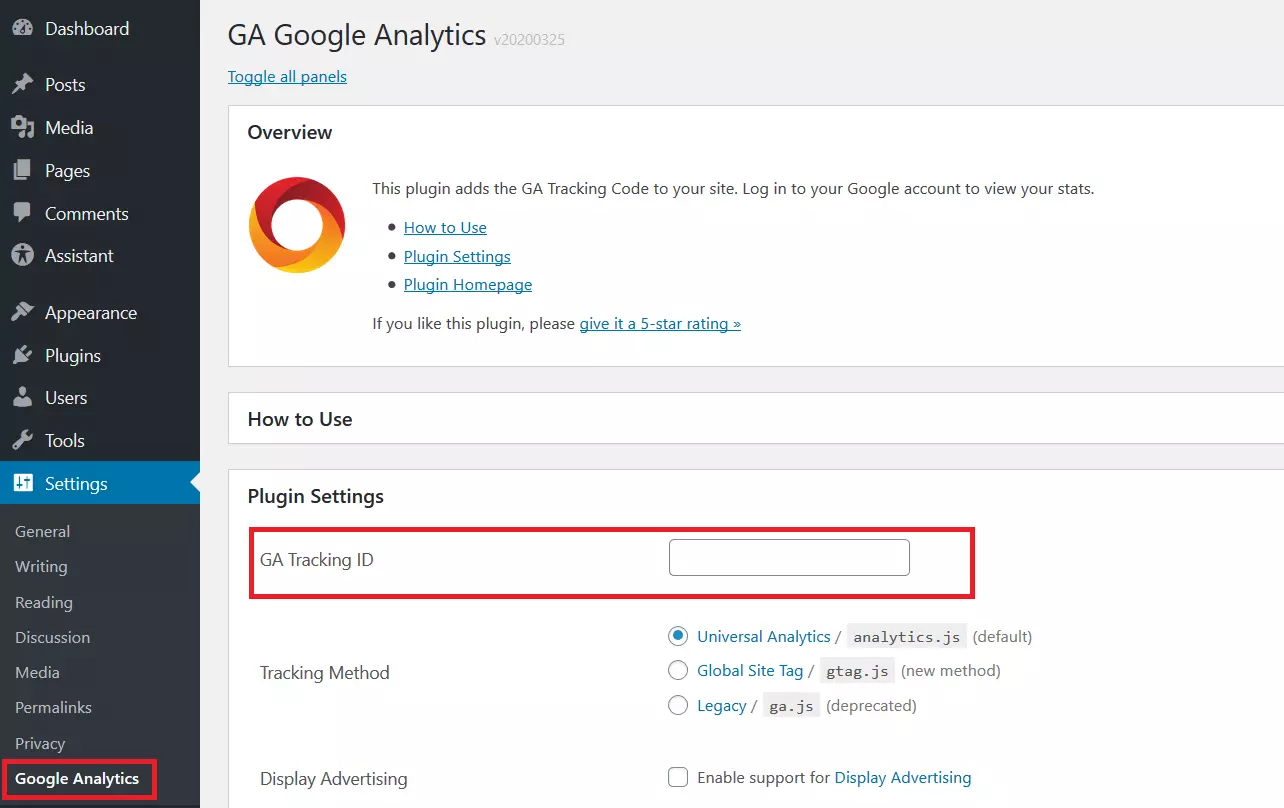
Once you install and activate the plug-in, you need to enter the Google Analytics tracking code into the settings. Open the Google Analytics tab from your WordPress dashboard. In the plug-in settings, add the tracking ID to the relevant field. Once you’ve entered the code, scroll to the bottom and click “Save changes”. Google Analytics should now be active on your WordPress site.
Google Analytics tracking code
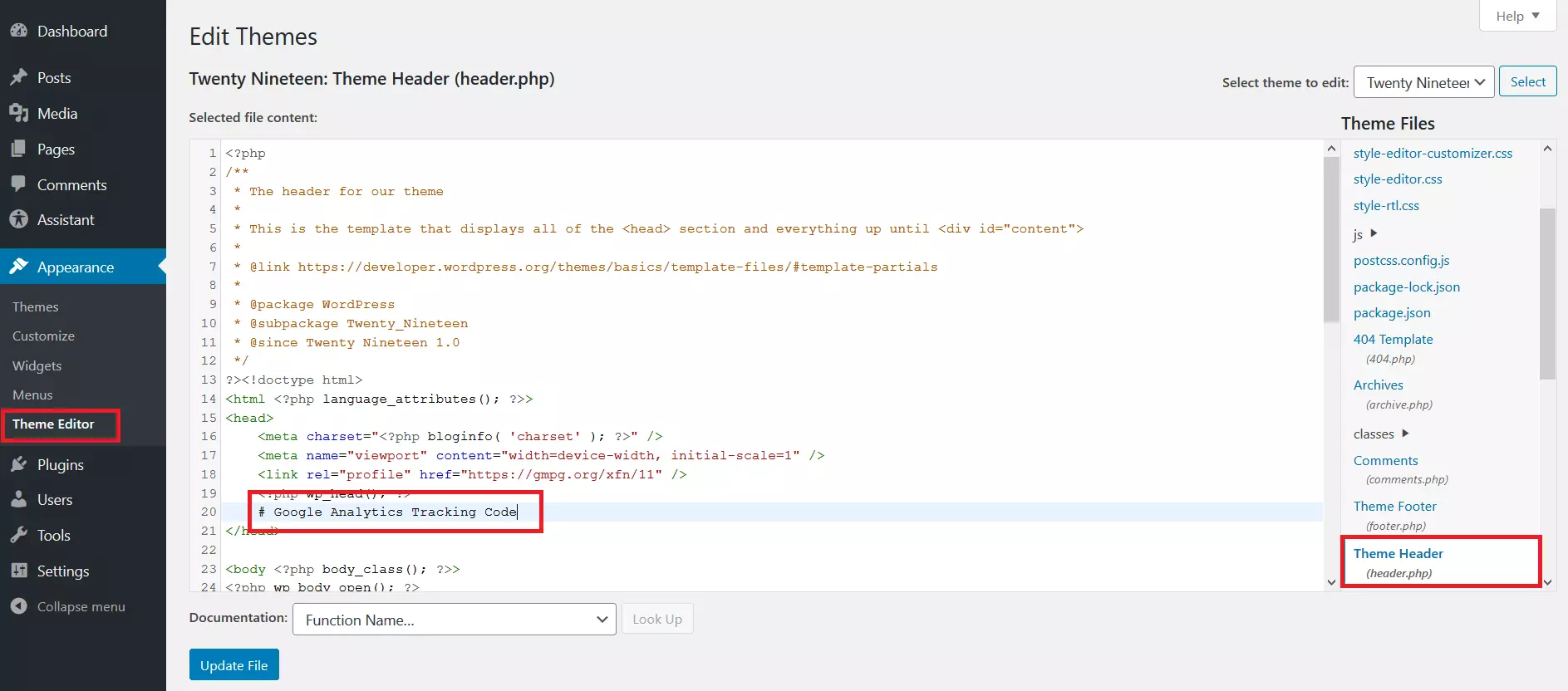
If you don’t want to use a plug-in, you can add the Google Analytics tracking code directly to your WordPress theme using the functions.php file. Here’s how.
When you’re manually adding a Google Analytics tracking code, it's important to make sure you use a child theme. This will stop the tracking code from being overwritten every time your WordPress theme updates.
A WordPress child theme is a theme that inherits features from another, “more important” theme. This other theme is called the parent theme.
Click on “Update file”. You have now added your Google Analytics tracking code to WordPress.
Google Tag Manager for WordPress
You also have the possibility to add Google Analytics to WordPress by using Google Tag Manager.
Google Tag Manager is a system to manage tags and code on your website to avoid you having to edit the code directly in WordPress. This reduces the chance of errors and lets you edit it even if you have no developer skills. To make the installation easier, you can get Google Tag Manager as a WordPress plug-in.
Download the plug-in, then install and activate it. Create your Google Tag Manager account and set up a new container. Go to the admin tab of your Google Tag Manager dashboard and look for a row of characters beginning with “GTM”. This is your container ID. Copy it. Go back to your WordPress site and access the settings of the Google Tag Manager tab. Here, paste your Google Tag Manager ID into the relevant field.
Every tag that you put into Google Tag Manager will now also work on your WordPress website thanks to the plug-in.
- Stress-free, no matter your skill level with easy AI tools
- Full customisation with themes and plugins
- Hassle-free updates and less admin
Google Analytics and data protection
Current European data protection laws (the GDPR) mean that Google Analytics can no longer collect data without first getting consent from site visitors. You must therefore take a few precautions to ensure that Google Analytics is using data collected from your site in a way that complies with this data protection law.
1. Sign a valid data processing agreement with Google
You can sign a data processing agreement directly through your Google Analytics account. For more information about this agreement, go to this Google support page.
2. Activate IP anonymisation
By adding an “_anonymizeIp” function to your tracking codes in the JavaScript library “ga.js”, you can ensure that the IP addresses of your visitors will never be completely saved. The final digits, which allow identification of the computer itself, will be replaced with a series of zeros. For more information about IP anonymisation, go to this Google support page.
3. Avoid the “User ID” function
In the latest version of Google's “Universal Analytics”, even more data are processed than with the standard version. You should make sure that the User ID function is deactivated. This function allows tracking across devices by letting site owners follow User IDs even more effectively, which does not comply with German data protection laws.
4. Deactivate the target group (or “remarketing”) function
You can change this setting in the Google Analytics options. For more information, go to this Google support page.
5. Let users deactivate add-ons
Visitors have the possibility to opt out of their user data being saved. This works with all common browsers, but not on mobile devices.
6. Let users opt out of cookies
With a simple click, users can block analytics tracking, including on mobile devices. A guide on implementing this using JavaScript (Disabling tracking) can be found in this Google article.
7. Limit data retention periods
Limit data retention periods in the settings (to 14 months maximum) and deactivate the “Reset on new activity” function.
8. Explain your data protection
In your data protection policy, make sure you clearly explain to your users if you use Google Analytics, and if so, what you do with it. Make sure to also detail the above-mentioned points, i.e., the data processing agreement, IP anonymisation and opt-out options (for browser plug-ins and cookies).
There are even more tools to analyse your site’s performance. Some alternatives to Google Analytics place more importance on data protection.